Docket #: S23-317
Hybrid plasmonic core-shell nanostructures for photocatalysis
Stanford researchers within the Dionne Lab have developed a method to use copper titanium dioxide core-shell nanoparticles for the light driven production of green fuels or removal of contaminants in water.
Current approaches to photocatalysis include semiconductors like titanium dioxide; however, they only absorb ultraviolet light, which forms less than 5% of the sunlight that reaches Earth. A promising approach is the use of hybrid plasmonic metal nanoparticle-semiconductor nanostructures, which are the strongest light absorbers per volume and have a highly tunable absorption cross-section that spans the entire visible and near-IR spectrum. Previous examples of plasmonic-semiconductor hybrids relied on noble metals like gold and silver, which prevented this technology from being scalable for real-world applications.
Stanford researchers instead use core-shell hybrid nanoparticles from earth-abundant copper and titanium precursors. This invention is a simple two step method that can use sunlight to drive photocatalysis. Used for water purification, this invention does not require maintenance, is effective against chemicals, plastics, and pathogens, and results in no toxic byproducts.
Stage of Development
Figure:
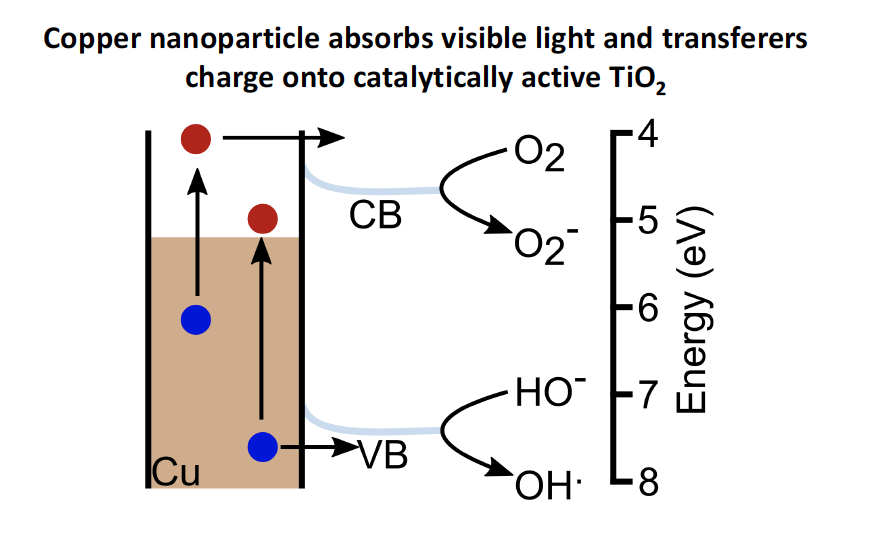
Figure description:Copper core absorbs light, and electrons are excited into higher energetic states, leaving behind holes. Electrons and holes are then transferred onto TiO2. TiO2 reduces CO2 into solar fuels and industrially useful chemicals (methanol, methane, ethylene). TiO2 also produces reactive oxygen species (ROS), which can remove contaminants in water.
Image credit: Inventors
Applications
- Green fuel production
- Water purification
- Plastic upcycling
Advantages
- Cost effective and scalable - current plasmonic-semiconductor hybrids rely on noble metals like gold and silver, whereas this method uses earth-abundant copper or nickel
- Direct solar to fuel production increase in overall efficiency and decrease in system size and complexity
- For water purification: Effective against chemicals, plastics, and pathogens
- Mineralizes contaminants, leaving behind no toxic byproducts
- Simple two step method that does not require maintenance or replacement
- No need to exchange filters or UV lamps
- No continuous supply of chemicals or electricity
Related Links
Similar Technologies
-
Alternative Energy with Efficient, Low-cost Mixing Entropy Battery S15-120Alternative Energy with Efficient, Low-cost Mixing Entropy Battery
-
Materials for low cost, scalable, thermochemical hydrogen production S16-325Materials for low cost, scalable, thermochemical hydrogen production
-
Plasmonic gas diffusion reactor for CO2 conversion to high-value chemicals S24-130Plasmonic gas diffusion reactor for CO2 conversion to high-value chemicals