Docket #: S22-196
Imaging system to enhance the visibility of cholesteatoma tissue and margins during surgery
Stanford researchers have developed a new method of imaging cholesteatoma, an expanding and destructive lesion of the middle ear and mastoid, based on its chemical composition. The researchers found that cholesteatoma tissue fluoresces under both 405 nm and 450 nm illumination, while mucosa tissue does not. They can utilize this signature to design an imaging system for surgical guidance.
Cholesteatomas are often asymptomatic and are difficult to detect, but if left untreated can erode adjacent bony structures, leading to severe complications such as brain abscesses, meningitis, facial nerve paralysis, and hearing loss. Cholesteatomas are treated by surgery, but frequently recur due to incomplete removal because of the difficulty of accurately visualizing the bounds of the lesion. This imaging system can distinguish between cholesteatoma and mucosa and similarly colored lesions and could help surgeons to more completely remove cholesteatomas.
Stage of Development
Figure:
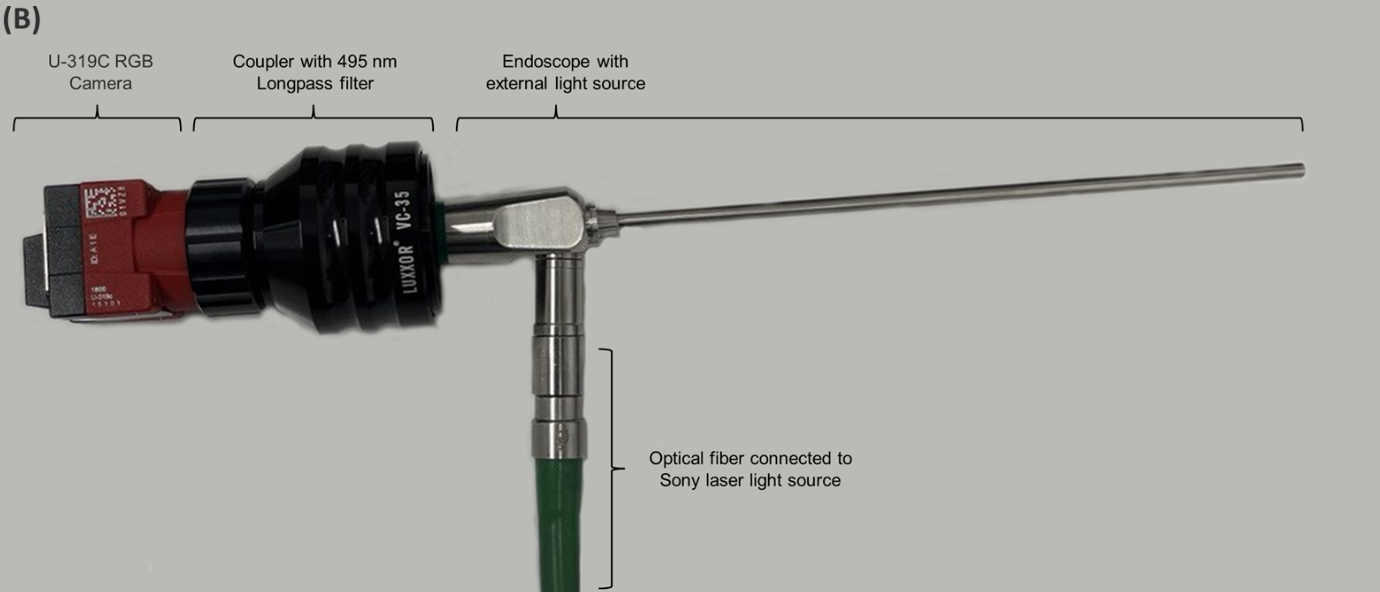
Figure description: Cholesteatoma imaging device
Image credit: Journal of Biomedical Optics, Vol. 28, Issue 6, (2023). https://doi.org/10.1117/1.JBO.28.6.066003
Applications
- Cholesteatoma surgery
Advantages
- Helps identify cholesteatoma at surgical site
- Distinguishes cholesteatoma from mucosa
Publications
- Stella Yang, Joyce Farrell, Shenglin Ye, Iram Ahmad, Tulio A Valdez. Imaging guidance for cholesteatoma surgery using tissue autofluorescence. (2023) J Biomed Opt., 28(6)
Related Links
Patents
- Published Application: WO2024216239
- Published Application: 20260033708
Similar Technologies
-
Catheter sensing technology that eliminates need for X-ray imaging during angiography S21-002Catheter sensing technology that eliminates need for X-ray imaging during angiography
-
Improved surgical navigation for robotic endoscopes and catheters S16-327Improved surgical navigation for robotic endoscopes and catheters
-
Diode-pumped photonic integrated titanium-sapphire waveguide amplifier S23-369Diode-pumped photonic integrated titanium-sapphire waveguide amplifier