Docket #: S16-257
Improving robot manipulation capabilities through workpiece contact state estimation
Stanford University and Honda Motor Co. have patented a device and method for estimating workpiece contact states during robotic manipulation tasks. Seemingly easy tasks like placing items in a box, is a challenge using robotics as the workpiece location during manipulation is unknown. (Figure 1.) Vision guided methods fail in confined and potentially blocked spaces. Using contact forces to guide robot motion is more suitable for manipulation.
In this patented technique, the contact force data coming from the sensor on the distal end of the robot arm is used to determine the workpiece location. A controller processes the force signals – translational force and/or moment - to successfully estimate the contact state. This patent is one of the outcomes of the project "Advanced Task Behaviors and Manipulation Capabilities for Humanoid Robots."
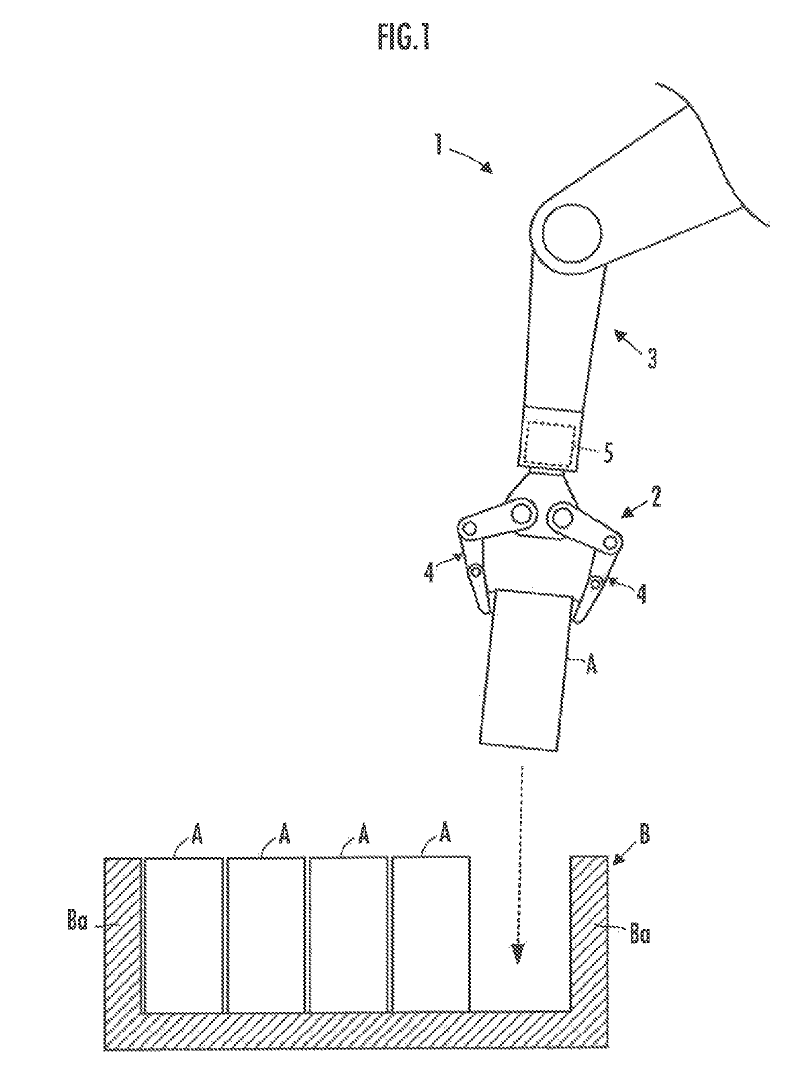
Figure 1 - Robot arm manipulating workpiece A into storage box B (force sensor located at 5)
Applications
- Robotics – especially for manufacturing robots
Advantages
- Improves robot manipulation performance
Related Links
Patents
- Published Application: 20180071915
- Issued: 10,213,925 (USA)
Similar Technologies
-
Tactile Gesture Interpretation for Safe Human-Robot Handovers S20-470Tactile Gesture Interpretation for Safe Human-Robot Handovers
-
Patterned and instrumented directional adhesives for enhanced gripping with industrial manipulators S17-318Patterned and instrumented directional adhesives for enhanced gripping with industrial manipulators
-
Third Arm: Smart, Wearable, Robotic device S18-211Third Arm: Smart, Wearable, Robotic device